
Nursing Diagnosis For Heart Failure Hear Choices
Written by Maegan Wagner, BSN, RN, CCM Heart failure (HF), sometimes referred to as Congestive Heart Failure (CHF), occurs when the heart can't supply blood effectively to the rest of the body. The left ventricle of the heart is larger and is responsible for most of the pumping action.

congestive_heart_failure_differential_diagnosis_map Nursing notes
This page contains the complete congestive heart failure nursing lecture e.g. (definition, pathophysiology,& more) ,nursing exam and nursing care plan.
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Nursing Care Plan & Management
1. Initiating Interventions for Decrease in Cardiac Output 2. Monitoring Diagnostic Procedures and Laboratory Studies 3. Administering Medication and Providing Pharmacological Interventions 4. Maintaining or Improving Respiratory Function 5. Managing Fluid Volume and Electrolyte Imbalance 6. Providing Perioperative Nursing Care 7.

Ncp Congestive Heart Failure Heart Failure Heart
Diagnosis. To diagnose heart failure, your health care provider examines you and asks questions about your symptoms and medical history. Your provider checks to see if you have risk factors for heart failure, such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease or diabetes. Your care provider listens to your lungs and heart with a device called.
Congestive Heart Failure CHF Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a severe condition that can be difficult to manage and requires comprehensive care. Without an effective nursing care plan, CHF patients may not receive the care they need to improve their quality of life. This can lead to further complications and even death.

NCP 60 Nursing Care Plan on Congestive Heart Failure/CHF/Cardiovascular
Upon physical assessment his breathing is shallow and labored, respiratory rate is 30 breaths per minute, heart rate 115 beats per minute, oxygen saturation 83% on room air, blood pressure 179/98 mm Hg, he has +4 pitting edema in bilateral lower extremities, and crackles are heard in his lung fields throughout.
Download Free Nursing books, ECG strips, PPT presentations, Videos and
Lets take a look at a concept map for congestive heart failure or CHF! So in this lesson we will take a look at the components of a concept map including contributing factors, medications, lab work and the significance, patient education, and associated nursing diagnoses with interventions and evaluations! Ok so here is a basic example of a.
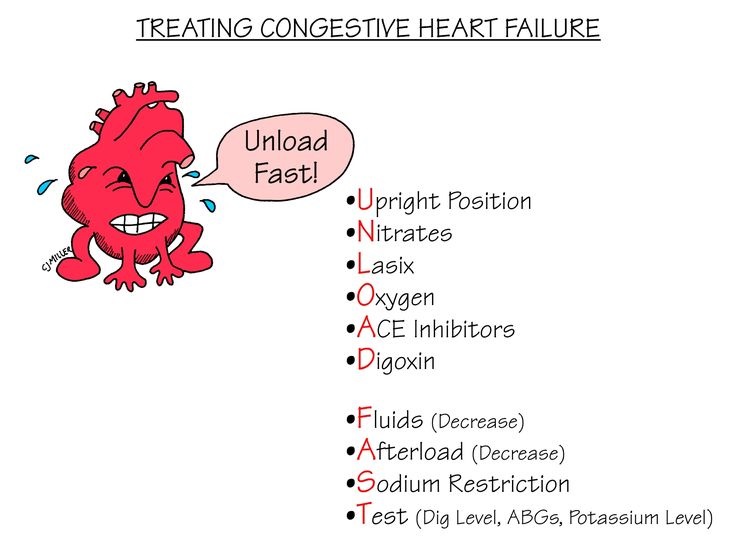
Nursing Mnemonics Treating Congestive Heart Failure StudyPK
Introduction. Heart failure is a common and complex clinical syndrome that results from any functional or structural heart disorder, impairing ventricular filling or ejection of blood to the systemic circulation to meet the body's needs. Heart failure can be caused by several different diseases. Most patients with heart failure have symptoms.

Congestive Heart Failure (NCP) Nursing Care Plan for CONGESTIVE HEART
Management. Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan. Congestive heart failure (CHF), otherwise known simply as heart failure (HF) is the medical term that describes the heart's inability to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow and meet the body's metabolic needs. This ineffective pumping leads to congestion of the venous circuit on both the.
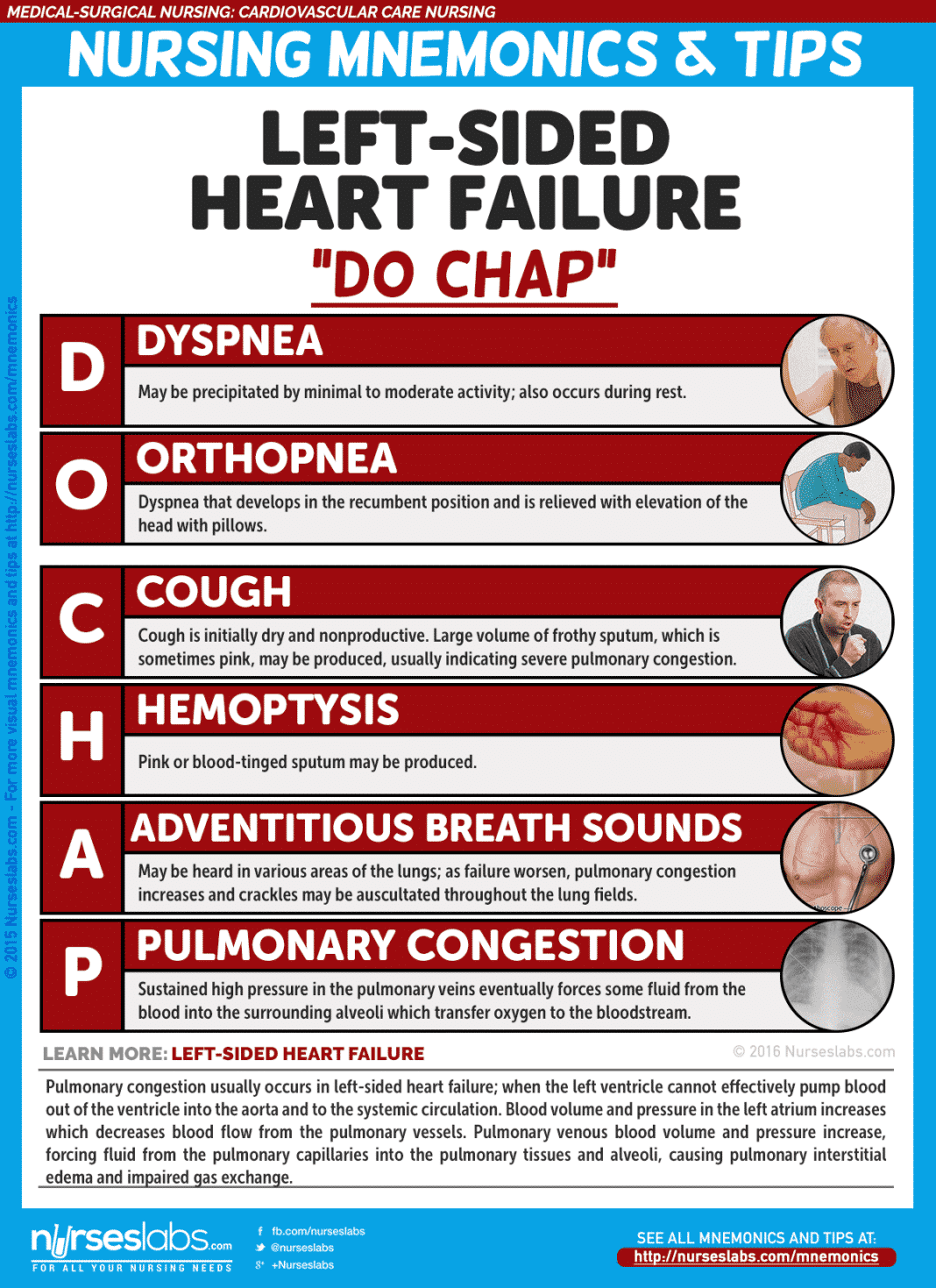
Heart Failure Nursing Care Management A Study Guide
To accomplish this aim, 53 terms were identified in the focus axis of the International Classification for Nursing Practice (ICNP®), which guided the construction of these statements using the guidelines of the International Council of Nurses and ISO 18. 104.
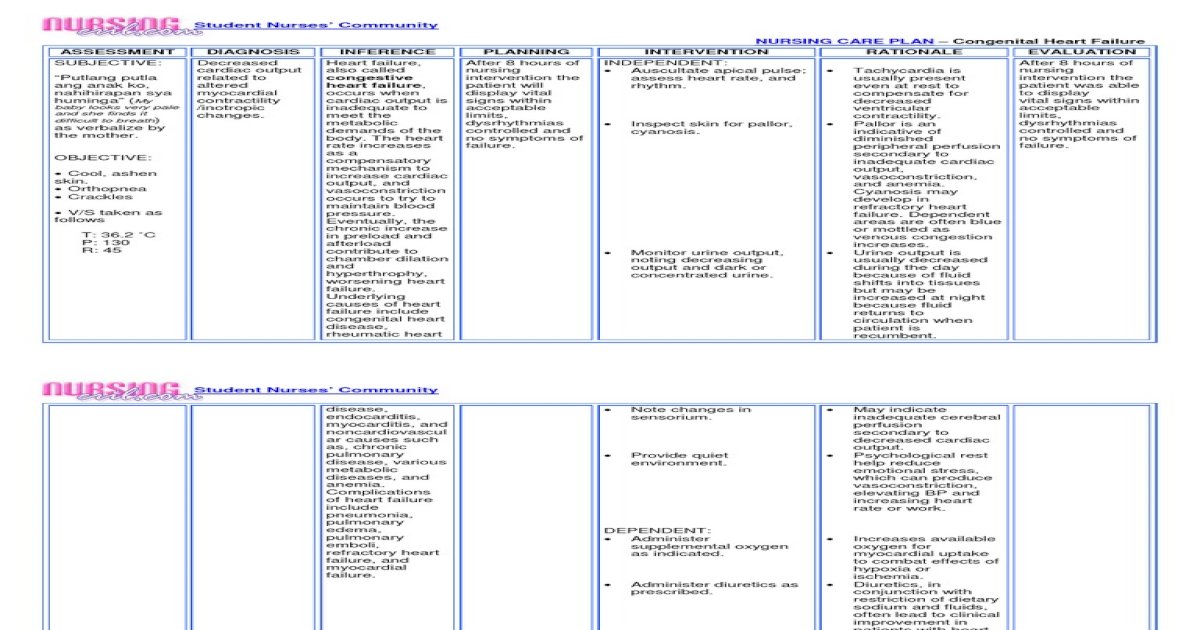
Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart Failure [PDF Document]
Abstract. In Brief. Heart failure (HF) is a chronic syndrome that requires patients to manage signs and symptoms and adhere to a complex medication regimen. This article discusses updates in HF care related to a universal definition and new therapies, focusing on the four pillars of therapy for HF with reduced ejection fraction.
Congestive Heart Failure Symptoms, Stages, Treatment, Diagnosis
Congestive heart failure causes substantial patient morbidity and mortality in the United States. Symptoms and physical findings can be helpful in diagnosis but have limited sensitivity and specificity. Objective measurement of ventricular function is essential in virtually all patients in whom a diagnosis of heart failure is suspected. Reversible causes of heart failure must be sought.

Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart Failure Heart
Key Roles for the Nurses in Acute Heart Failure Management. Rapid triage to appropriate environment for safe clinical care: coronary care unit, cardiology ward, general medical ward. Objective monitoring for change in signs and symptoms suggestive of response to treatment. Promptly identify and address relevant changes in clinical status.

Figure 1 from Clinical care for the patient with heart failure a
Outline Objective for Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) What is Congestive Heart Failure? Imagine your heart is like a pump in a garden watering system. In Congestive Heart Failure, this pump isn't working as well as it should. It doesn't mean the heart has stopped working, but it's struggling to pump blood efficiently.

Care Plan For Congestive Heart Failure
Congenital heart defects. Faulty heart chambers or valves at birth can directly affect the functionality of the heart. Other heart conditions. Viral infections such as COVID-19 may cause inflammation of the cardiac muscles known as myocarditis.

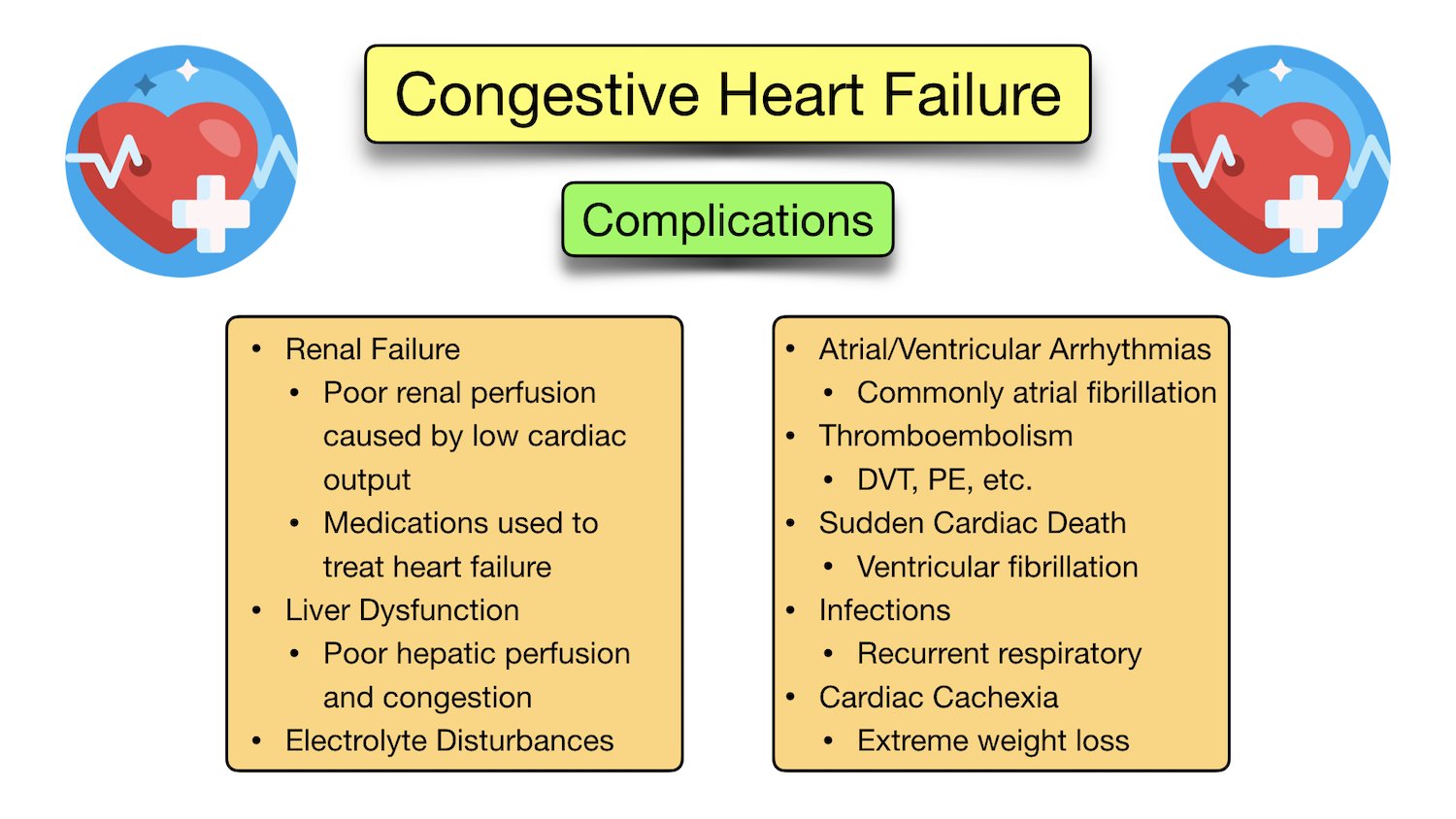
Congestive Heart Failure infograph CLICK to enlarge picture for better
Objective: to develop an ICNP® terminology subset for the care of people with heart failure. Methods: this is a methodological study, which used the theoretical framework of the Mid-Range Nursing.